Chapter 16: Ajax
CS 80: Internet Programming
Instructor: Mark Edmonds
What is Ajax?
-
Asynchronous
Javascript And
XML
- Misleading name! Originally developed for XML, but you can transfer plain text or JSON with it as well.
What is Ajax?
- The idea: we load data as the user is viewing and interacting with the page; Javascript communicates with the server in the background to update the page.
- The effect: web applications that behave much more similarly to desktop applications
- The benefit: web applications don't have to reload a page to get new data. This can be incredibly simple data or complex data to enable drastic changes to the page
What is Ajax?
- A side note about practicality:
- We will learn about Ajax, but running Ajax requires a webserver to respond to requests. We will eventually cover webservers which will enable us to run our own basic Ajax examples
Ajax Basics
- "Raw" Ajax uses Javascript directly to send asynchronous requests to the server, and updates the webpage using DOM
- There are a lot of cross-browser, cross-operating
system considerations you have to handle when using raw
Ajax
- Instead, jQuery, ASP.NET Ajax, etc can provide easy-to-use cross-platform support
Ajax basics
-
XMLHttpRequest- object that manages the interaction between the server and the webpage (without reloading)- Abbreviated
XHR
- Abbreviated
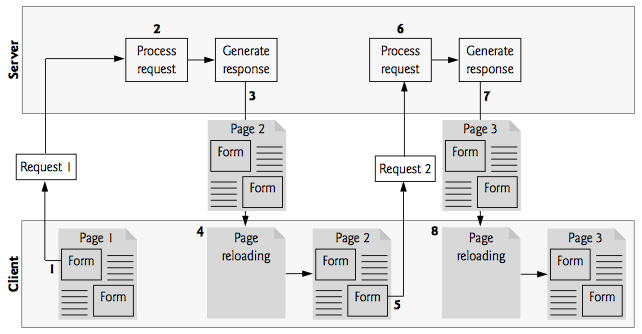
Traditional Webpage
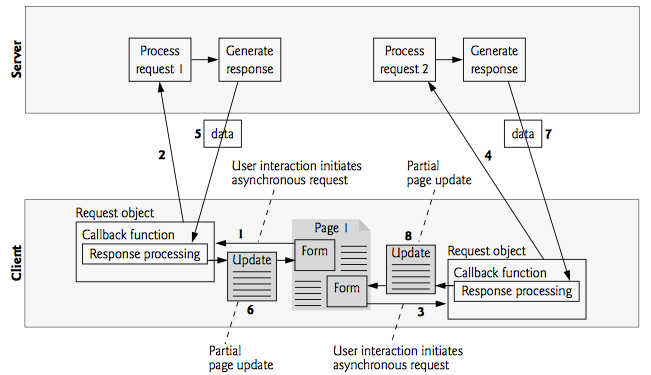
Ajax Webpage
Ajax Steps
- Client creates XHR object
- XHR sends a request to the server and waits for a
response
- These requests are made asynchronously, which means the user can keep interacting with the web page while the request finishes
- Many things can happen here, client could interact more with the webpage, create new XHR requests, etc
- Server replies to the request in step 2
- Client executes a callback function, which processes the data recieved in step 4 (could modify the DOM, etc). Commonly a partial page update
Ajax Basics
- This process is asynchronous, so tracking the exact execution can be difficult. Lots of things could happen during step 3 above
Conceptual Example - Validating a form
- We can accomplish a lot of this using the new HTML5 forms, but provides more generic form support
- We can validate any type of form data (e.g. zip code, etc), asynchronously, as the user fills in the form.
- Enables a more powerful form model, you see this all the time online!
Example - SwitchContent
- The basic concept: when the user puts their mouse over a textbook cover, we load that textbook's corresponding information
Example: SwitchContent.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<!-- Fig. 16.5: SwitchContent.html -->
<!-- Asynchronously display content without reloading the page. -->
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style type="text/css">
.box {
border: 1px solid black;
padding: 10px
}
</style>
<title>Switch Content Asynchronously</title>
<script>
var asyncRequest; // variable to hold XMLHttpRequest object
// set up event handlers
function registerListeners() {
var img;
img = document.getElementById("cpphtp");
img.addEventListener("mouseover",
function() {
getContent("cpphtp8.html");
});
img.addEventListener("mouseout", clearContent);
img = document.getElementById("iw3htp");
img.addEventListener("mouseover",
function() {
getContent("iw3htp.html");
});
img.addEventListener("mouseout", clearContent);
img = document.getElementById("jhtp");
img.addEventListener("mouseover",
function() {
getContent("jhtp.html");
});
img.addEventListener("mouseout", clearContent);
img = document.getElementById("vbhtp");
img.addEventListener("mouseover",
function() {
getContent("vbhtp.html");
});
img.addEventListener("mouseout", clearContent);
img = document.getElementById("vcshtp");
img.addEventListener("mouseover",
function() {
getContent("vcshtp.html");
});
img.addEventListener("mouseout", clearContent);
img = document.getElementById("javafp");
img.addEventListener("mouseover",
function() {
getContent("javafp.html");
});
img.addEventListener("mouseout", clearContent);
} // end function registerListeners
// set up and send the asynchronous request.
function getContent(url) {
// attempt to create XMLHttpRequest object and make the request
try {
asyncRequest = new XMLHttpRequest(); // create request object
// register event handler
asyncRequest.addEventListener(
"readystatechange", stateChange);
asyncRequest.open("GET", url, true); // prepare the request
asyncRequest.send(null); // send the request
} // end try
catch (exception) {
alert("Request failed.");
} // end catch
} // end function getContent
// displays the response data on the page
function stateChange() {
if (asyncRequest.readyState == 4 && asyncRequest.status == 200) {
document.getElementById("contentArea").innerHTML =
asyncRequest.responseText; // places text in contentArea
} // end if
} // end function stateChange
// clear the content of the box
function clearContent() {
document.getElementById("contentArea").innerHTML = "";
} // end function clearContent
window.addEventListener("load", registerListeners);
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Mouse over a book for more information.</h1>
<img id="cpphtp" alt="C++ How to Program book cover" src="cpphtp8.jpg">
<img id="iw3htp" alt="Internet & WWW How to Program book cover" src="iw3htp5.jpg">
<img id="jhtp" alt="Java How to Program book cover" src="jhtp9.jpg">
<img id="vbhtp" alt="Visual Basic 2010 How to Program book cover" src="vb2010htp.jpg">
<img id="vcshtp" alt="Visual C# 2010 How to Program book cover" src="vcsharp2010htp.jpg">
<img id="javafp" alt="Java for Programmers book cover" src="javafp.jpg">
<div class="box" id="contentArea"></div>
</body>
</html>
Example - SwitchContent
- What's doing all the Ajax heavy lifting?
getContentandstateChange
Pelimaries: Exceptions
- Exceptions indicate an error happened during data processes, but allow the program to continue running if the error is "handled"
- We refer to "handling" an error as catching an exception
- We refer to indicating an error occured as throwing an exception
Pelimaries: Exceptions
- When we want to catch an exception, we acknowledge an
error by happen by wrapping the relevant portion of code
in a
try...catchblock- We put code that might cause the exception in the
tryportion - We put error-recovery code in the
catchblock - The try block will always execute (that's the code we are trying to run)
- The catch block will only run if an exception is thrown
- We put code that might cause the exception in the
Pelimaries: Exceptions
-
Syntax
// syntax for trying a block of code and catching an exception try { // code that might throw an exception } catch (exception) { // error recovery code }
getContent
- Creates a raw Ajax object
- Registers the function
stateChangeas the callback functino for thereadystatechangeevent- The
readystatechangeevent is triggered when the value of of the XHR'sreadyStateproperty is changed -
readyStatecan be 5 values: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/XMLHttpRequest/readyState - A related property,
statuscontains the HTTP status code of the HTTP request (200 = success)
- The
getContent
- Opens the url and specifies the HTTP request with the
GET method, and
truesays to do this operation aynschronously- Basically creates the HTTP request
- Send the HTTP request
stateChange
- The conditional statement makes sure that the aync
request is completed.
- Question: when will the
stateChangefunction get called? How many times will it get called?
- Question: when will the
- Body of the state change processes the data from the request.
Running SwitchContent
- If you want to run this example, download the files from the ch16 examples
- But this isn't enough, we need an actual webserver to respond to the Ajax request
- We can start a simple webserver (using any python
console) with
python -m http.server(Python 3) orpython -m StimpleHTTPServer(Python 2) from the folder with our examples downloaded - Then navigate to
http://localhost:8000/SwitchContent.htmlin your web browser
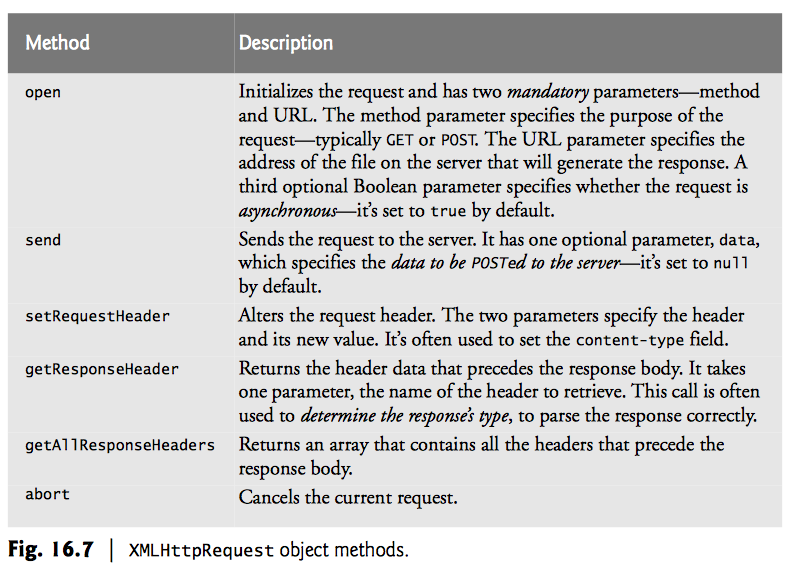
Ajax Events and Objects

Ajax Methods
Ajax, XML, and DOM
- When XHR receives XML data, it is stored as an XML DOM obejct (tree)
- This is best explained with the following example
Example: PullImagesOntoPage.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<!-- Fig. 16.8: PullImagesOntoPage.html -->
<!-- Image catalog that uses 1Ajax to request XML data asynchronously. -->
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title> Pulling Images onto the Page </title>
<style type="text/css">
li {
display: inline-block;
padding: 4px;
width: 120px;
}
img {
border: 1px solid black
}
</style>
<script>
var asyncRequest; // variable to hold XMLHttpRequest object
// set up and send the asynchronous request to get the XML file
function getImages(url) {
// attempt to create XMLHttpRequest object and make the request
try {
asyncRequest = new XMLHttpRequest(); // create request object
// register event handler
asyncRequest.addEventListener(
"readystatechange", processResponse, false);
asyncRequest.open("GET", url, true); // prepare the request
asyncRequest.send(null); // send the request
} // end try
catch (exception) {
alert('Request Failed');
} // end catch
} // end function getImages
// parses the XML response; dynamically creates an undordered list and
// populates it with the response data; displays the list on the page
function processResponse() {
// if request completed successfully and responseXML is non-null
if (asyncRequest.readyState == 4 && asyncRequest.status == 200 &&
asyncRequest.responseXML) {
clearImages(); // prepare to display a new set of images
// get the covers from the responseXML
var covers = asyncRequest.responseXML.getElementsByTagName(
"cover")
// get base URL for the images
var baseUrl = asyncRequest.responseXML.getElementsByTagName(
"baseurl").item(0).firstChild.nodeValue;
// get the placeholder div element named covers
var html_covers = document.getElementById("covers");
// create an unordered list to display the images
var imagesUL = document.createElement("ul");
// place images in unordered list
for (var i = 0; i < covers.length; ++i) {
var cover = covers.item(i); // get a cover from covers array
// get the image filename
var image = cover.getElementsByTagName("image").
item(0).firstChild.nodeValue;
var title = cover.getElementsByTagName("title").
item(0).firstChild.nodeValue;
// create li and img element to display the image
var imageLI = document.createElement("li");
var imageTag = document.createElement("img");
// set img element's src attribute
imageTag.setAttribute("src", baseUrl + encodeURI(image));
imageTag.setAttribute("alt", title);
imageLI.appendChild(imageTag); // place img in li
imagesUL.appendChild(imageLI); // place li in ul
} // end for statement
html_covers.appendChild(imagesUL); // append ul to covers div
} // end if
} // end function processResponse
// clears the covers div
function clearImages() {
document.getElementById("covers").innerHTML = "";
} // end function clearImages
var global_name = "all.xml";
// register event listeners
function registerListeners() {
document.getElementById("all").addEventListener(
"click",
function() {
getImages("all.xml");
}, false);
document.getElementById("simply").addEventListener(
"click",
function() {
getImages(global_name);
}, false);
document.getElementById("howto").addEventListener(
"click",
function() {
getImages("howto.xml");
}, false);
document.getElementById("dotnet").addEventListener(
"click",
function() {
getImages("dotnet.xml");
}, false);
document.getElementById("javaccpp").addEventListener(
"click",
function() {
getImages("javaccpp.xml");
}, false);
document.getElementById("none").addEventListener(
"click", clearImages, false);
} // end function registerListeners
window.addEventListener("load", registerListeners, false);
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="radio" name="Books" value="all" id="all"> All Books
<input type="radio" name="Books" value="simply" id="simply"> Simply Books
<input type="radio" name="Books" value="howto" id="howto"> How to Program Books
<input type="radio" name="Books" value="dotnet" id="dotnet"> .NET Books
<input type="radio" name="Books" value="javaccpp" id="javaccpp"> Java/C/C++ Books
<input type="radio" checked name="Books" value="none" id="none"> None
<div id="covers"></div>
</body>
</html>